Tech Lead
케어링
Role
AI, Devops, Backend, Frontend
Tasks
- • 시스템 개발 총괄
- • 전사 클라우드 아키텍처 설계, 운영
- • 전사 CI/CD 파이프라인 구축
I'm a Software Engineer from Seoul, Korea.
I enjoy exploring new development areas and bringing projects to life.
When I'm not working, I spend quality time with my family.
AI, Devops, Backend, Frontend
Devops, Backend
Backend, Frontend
Backend, Frontend, Android, iOS
Backend, Frontend
Backend, Frontend
Backend
Backend, Frontend

AI 기반 FC 온라인 전적 분석 및 전술 코칭 서비스
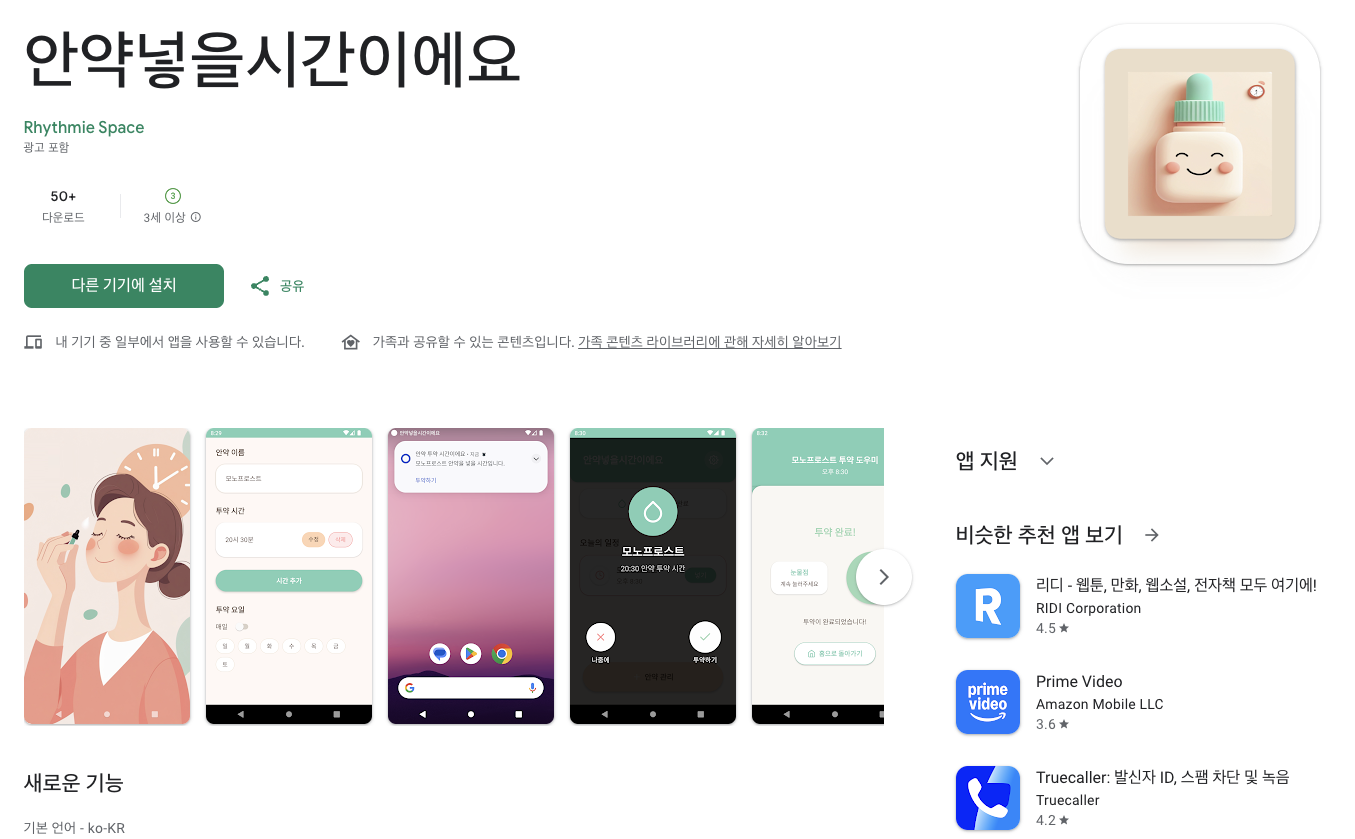
매일 사용하는 안약의 복용 시간을 잊지 않도록 도와주는 투약 알림 도우미 앱
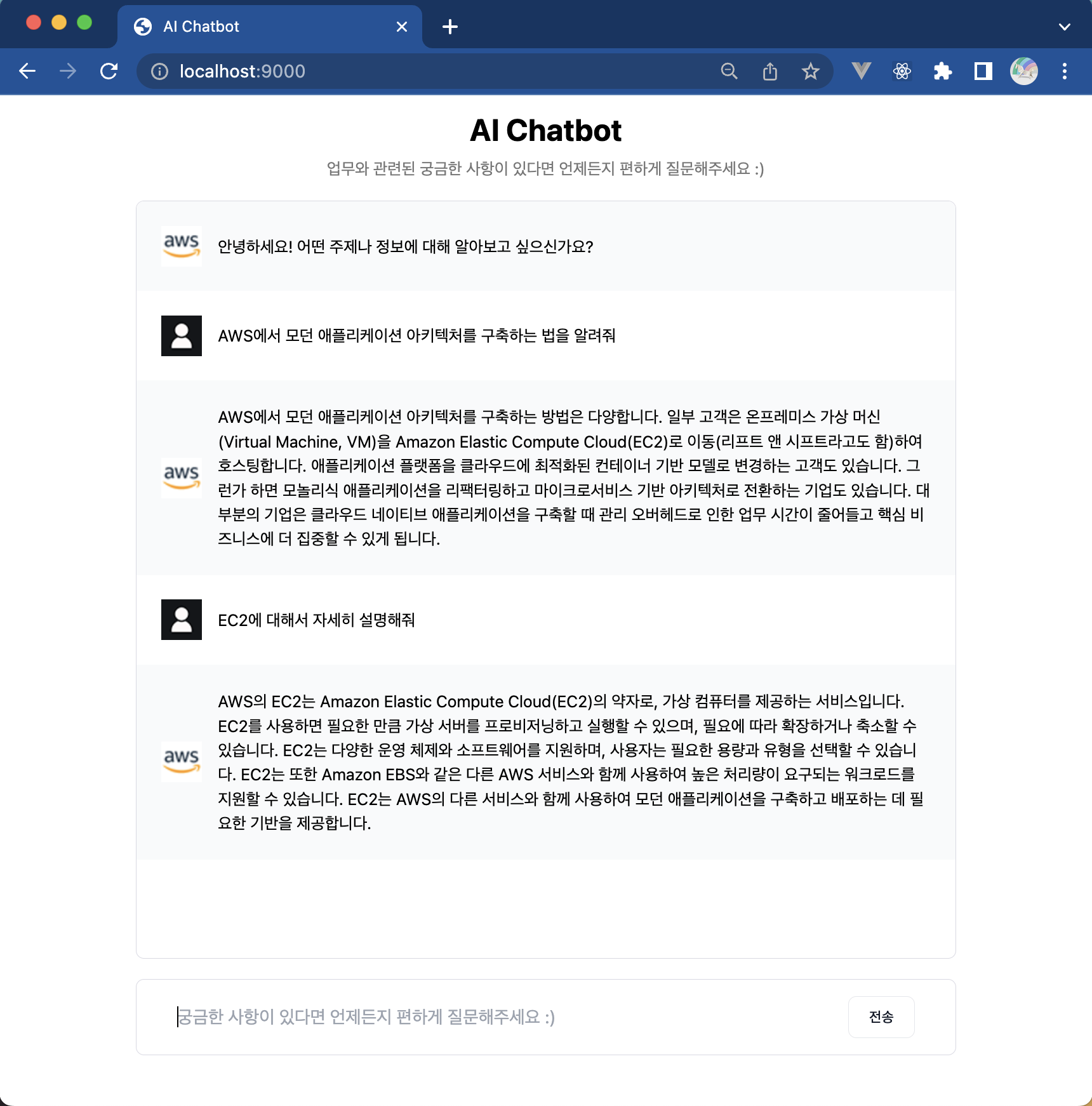
FastAPI + LangChain을 이용한 질문-응답 시스템

AWS Lightsail과 WordPress를 활용한 벤처캐피털 기업 홈페이지
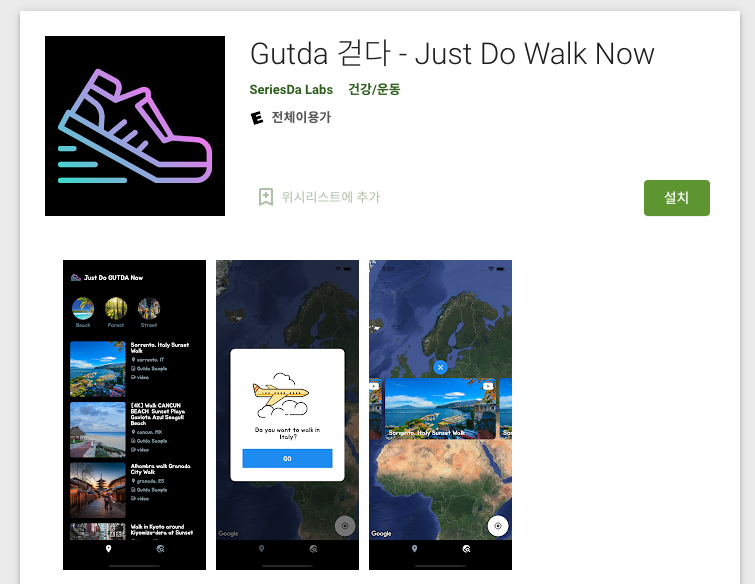
걷기를 통해 건강한 라이프스타일을 장려하는 게이미피케이션 기반 걷기 동기 부여 앱

Spring Boot와 Spring Security를 이용한 JWT 인증과 인가 튜토리얼 강의
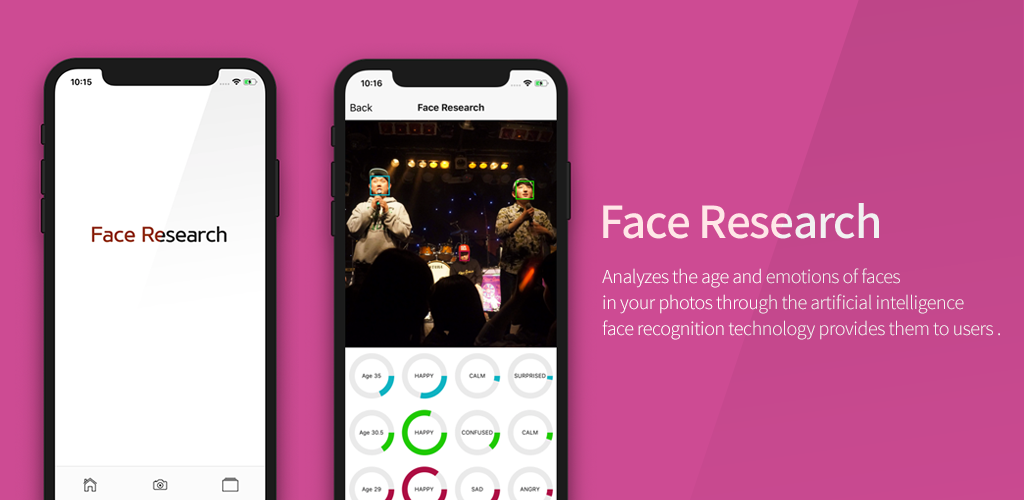
아마존 AI 기술을 활용한 얼굴 나이 및 감정 분석 모바일 앱
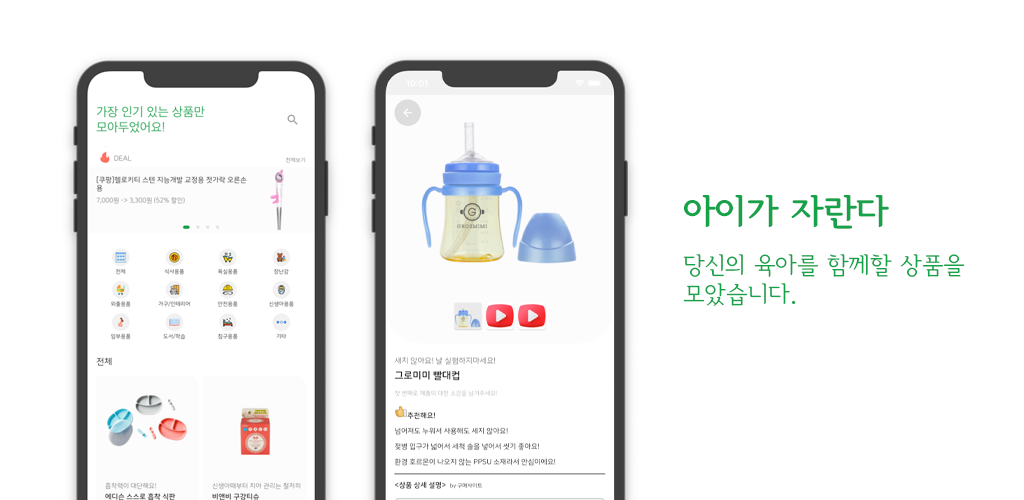
부모를 위한 종합적인 육아 성장 추적 앱 - 아이의 발달 과정과 성장을 기록하고 분석
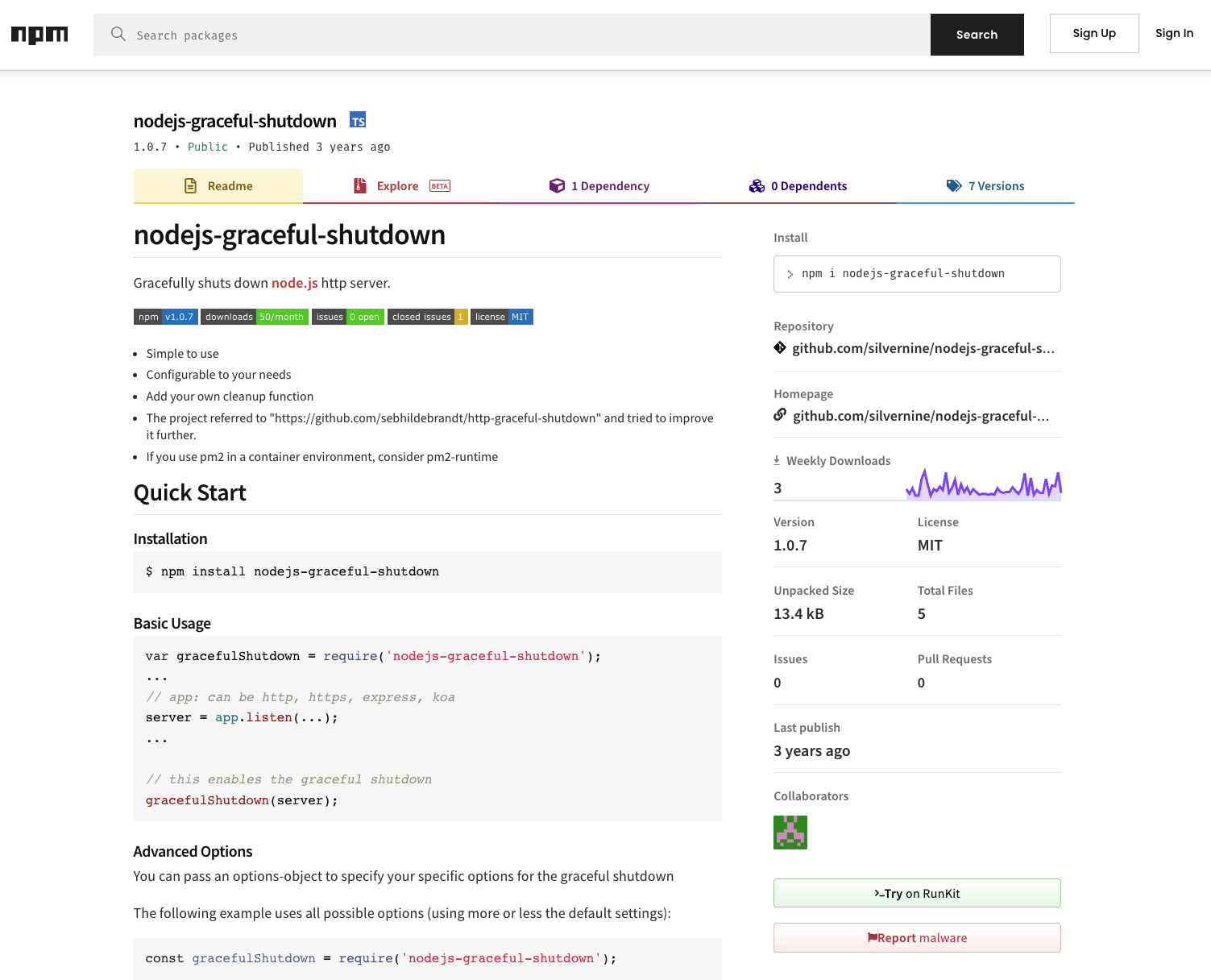
Node.js 애플리케이션에서 우아한 종료 기능을 구현하기 위한 경량 NPM 패키지
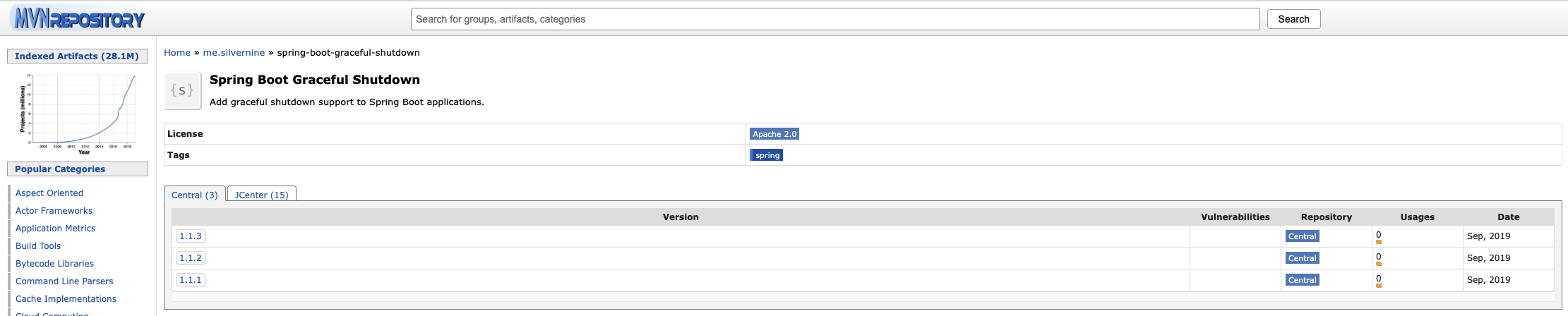
Spring Boot 애플리케이션에서 우아한 종료 메커니즘을 구현하기 위한 Java 라이브러리
실시간 모니터링 기능이 있는 Bluetooth 비콘 스캔 및 관리 iOS 애플리케이션
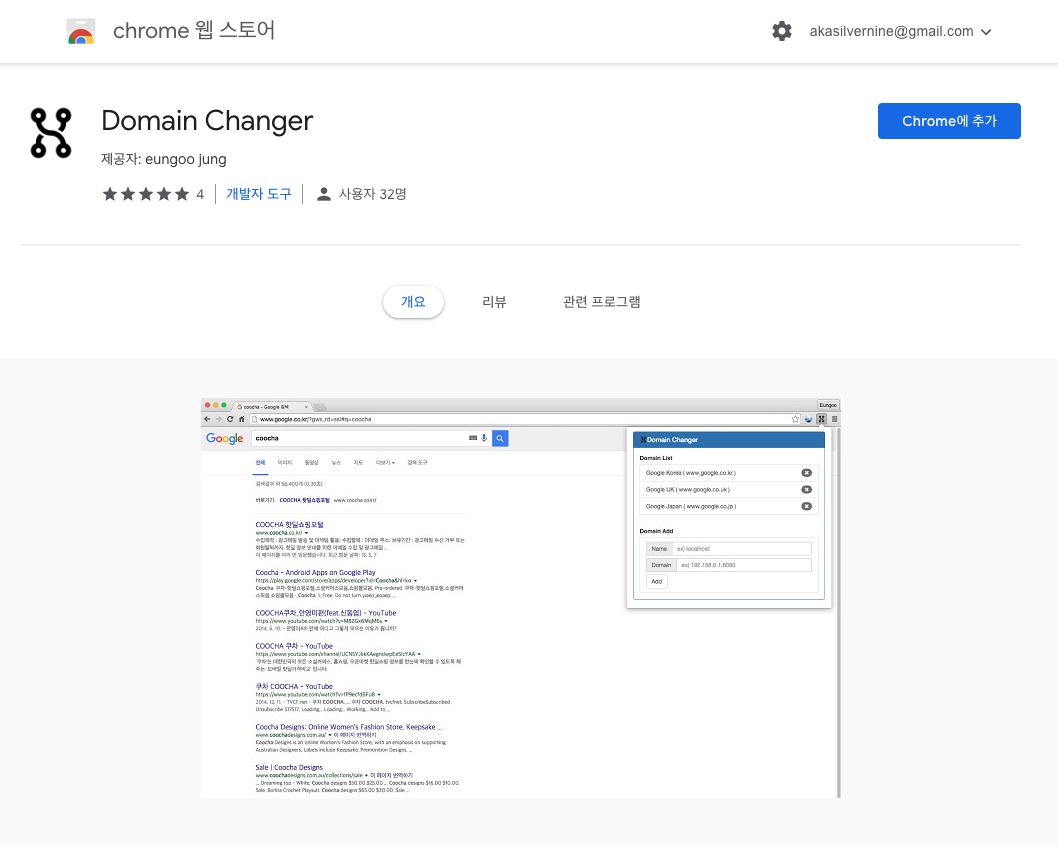
웹 개발 및 테스트를 위해 다양한 도메인 간 빠른 전환을 제공하는 Chrome 브라우저 확장 프로그램
Wowza Streaming Engine 인증 및 액세스 제어를 위한 보안 토큰 생성 NPM 패키지